Ultrasonographic Findings in Fetal neck and
chromosomal aberrations
S.Degani
Ultrasonographic Findings in Fetal neck and
chromosomal aberrations

S.Degani
Nuchal translucency
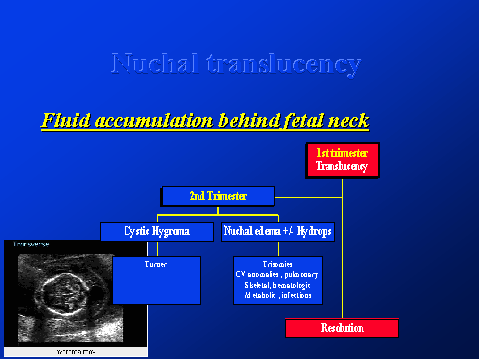
Nuchal translucency
Fluid accumulation behind fetal neck
Nuchal translucency
Physiological basis
Nuchal Translucency
Pathology:
Nuchal translucency
Measurement:
tissue.
Nuchal translucency
To determine significance of ultrasonographic marker : prevalence of the abnormality at different gestational age and maternal age.
2nd trimester fetus with Down Syndrome
Sensitivity=42% , Specificity 99.9%
Nuchal fold (2nd trimester)
Prospective studies:
Crane et al: >5 mm (14-18 wks)
>6 mm (19-24 wks)
Nuchal fold thickening:
Lateral neck cysts
Etiology?? Histology??
Nuchal translucency
20 small series (early 90s):
Nuchal translucency
Screening studies in high risk pregnancies:
(before karyotyping, mainly for maternal age)
Nuchal translucency
The prevalence of chromosomal aberrations is dependant on both NT thickness
&
maternal age.
Nuchal translucency
Screening unselected population:
Frimley Park Hosp. & St Peter’s Hospital:
Nuchal translucency
Austrian study:
Nuchal translucency
The multicenter screening study:
20,804 pregnancies; 164 chromosomal aberrations:
Nuchal translucency
Nuchal translucency
The multicenter study (III):
“Combining maternal age with fetal NT thickness is currently the most sensitive method of screening for chromosomal abnormalities”.
Nuchal translucency
University College study:
(1704 women , TAS at 8-14 weeks)
![]()